12 Causas de la Inflamación Crónica
In my last two posts I’ve been talking about chronic inflammation. First I discussed how diet can cause inflammation and chronic pain, and then I discussed what chronic inflammation is and how it can cause many health conditions including cancer, atherosclerosis, and type 2 diabetes.
Esta semana, aprenderemos sobre las 12 causas más comunes de inflamación crónica. ¡La buena noticia es que la mayoría de ellos son altamente controlables o completamente evitables!
Hábitos de estilo de vida:
- Dieta
- Tabaquismo y consumo de tabaco
- Consumo de alcohol
- Falta de ejercicio
- Hábitos de sueño
Estados internos:
- estrés
- Obesidad
- Condiciones autoinmunes
- Variantes genéticas
Desencadenantes externos:
- Infecciones virales y bacterianas.
- Alergenos y toxinas en los alimentos que comemos
- Exposición prolongada a irritantes, como aire contaminado y productos químicos industriales.
Señales de que puede tener inflamación crónica
Tener incluso uno de estos síntomas puede ser una indicación de que la respuesta inflamatoria ocurre constantemente en su cuerpo y / o cerebro:
- Grasa abdominal
- Nivel alto de azúcar en sangre
- Niebla del cerebro
- Dolores de cabeza
- Depresión
- Rigidez o dolor articular
- Artritis
- Fatiga
- Asma
- Problemas digestivos que incluyen gases, hinchazón, diarrea o estreñimiento
- Problemas de la piel que incluyen eccema, psoriasis, picazón o enrojecimiento
- Alergias o síntomas de alergia, como ojos llorosos y secreción nasal (producción excesiva de moco)
- Hinchazón en la cara o debajo de los ojos.
- Enfermedad de las encías
- Disfunción eréctil
1. Dieta
More and more research shows how the standard American diet, heavy in animal products, processed food, and added sugar and salt triggers the inflammation response in our body. Even if you live an otherwise healthy lifestyle and maintain a healthy weight, eating these foods puts you at risk for many inflammatory conditions including cancer, heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease, depression, and painful autoimmune diseases.
The worldwide trend toward a plant-based diet is encouraging—everyone from doctors to top athletes are recognizing the health benefits of eliminating animal products and processed food. The dramatic effects of eating a whole food, plant based diet—like complete recoveries from kidney disease, heart disease, thyroid disease, painful autoimmune diseases, diabetes, asthma, migraines, and even cancer—are hard to ignore.
2. Tabaquismo y consumo de tabaco
Toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke (including arsenic, ammonia, radon, and carbon monoxide) and smokeless tobacco (including formaldehyde, cyanide, arsenic, and lead) damage the cells in our body, triggering the immune response of inflammation. Cells are also damaged when chemicals from cigarette smoke combine with oxygen in the body, creating oxidative stress. In addition, nicotine by itself triggers an immune response in our cells.
The health effects of smoking and tobacco use are frightening. Since smoking kills more Americans than alcohol, car accidents, HIV, guns, and illegal drugs combined, your best bet is to avoid it completely.
3. Consumo de alcohol
There are at least three ways in which alcohol causes chronic inflammation. First, alcohol damages the cells in our body, triggering the immune response of inflammation. Second, metabolism of alcohol leads to the production of reactive oxygen species, which then stimulate inflammation. Third, hypoxia (lack of oxygen in tissues) resulting from alcohol metabolism can cause inflammation.
Keep in mind that the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services defines moderate drinking as being up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men. This falls to just one drink per day for both men and women over age 65.
A 2018 study of alcohol consumption in 195 countries showed that having just one alcoholic drink per day increases your chances of dying or suffering from cancer, stroke, heart disease, car accident, liver disease, and tuberculosis. While alcohol has been shown to have a mild protective effect against heart disease and diabetes, this effect is offset by the increased risk of cancer. The researchers who conducted the study concluded that the “level of consumption that minimizes health loss due to alcohol use is zero.”
4. Falta de ejercicio
Grandes estudios basados en la población muestran consistentemente que el ejercicio aeróbico regular disminuye la inflamación crónica. Hay al menos tres razones por las que:
1. By reducing body fat. As you’ll learn in #7, excess fat tissue creates the inflammatory response.
2. By contracting muscles and increasing muscle mass. During exercise, working muscles produce molecules that have anti-inflammatory effects.
3. By strengthening the immune system, making our acute immune response more efficient and effective. This reduces the chances that we’ll experience repeat or prolonged infections and the accompanying chronic inflammation.
5. Hábitos de sueño
Sleep is a critical part of our overall health, and one that many of us ignore. It might surprise you that too little sleep, too much sleep, and chronically disturbed sleep all increase levels of inflammatory markers in the body, in as little as one night.
Una de las razones de esto son nuestros ritmos circadianos: estos cambios fisiológicos que siguen un ciclo diario ayudan a regular nuestro sueño y vigilia, las hormonas, el apetito, la digestión, la temperatura corporal y, lo adivinó, nuestro sistema inmunológico. Los ritmos circadianos irregulares se han relacionado con afecciones inflamatorias crónicas que incluyen obesidad, diabetes y depresión.
A second way that sleep increases inflammation is by increasing stress, which triggers our immune response. A third way that sleep increases inflammation is by affecting gut health. Lack of quality sleep can change the makeup of our microbiota, increasing disease-causing bacteria and decreasing beneficial bacteria.
6. Estrés
Stress is a risk factor in 75% to 90% of disease, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic disease, depression, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and cancer.
The reason for this is that stress activates our immune response, triggering inflammation in both our body and brain. While acute stress can have a temporary positive effect on immune system function, chronic stress—the kind that the majority of us experience—has negative effects.
El estrés y la personalidad y los hábitos que lo impulsan, como ser tipo A y trabajar muchas horas, a menudo son admirados en nuestra sociedad. Si no estamos estresados, ¡no debemos trabajar lo suficiente! Pero el estrés crónico es tan perjudicial para nuestra salud como la obesidad y el tabaquismo, y reducir el estrés en su vida es una de las mejores cosas que puede hacer por su salud. (Me apasiona este tema y haré una serie de publicaciones sobre el estrés más adelante este otoño, ¡estad atentos!)
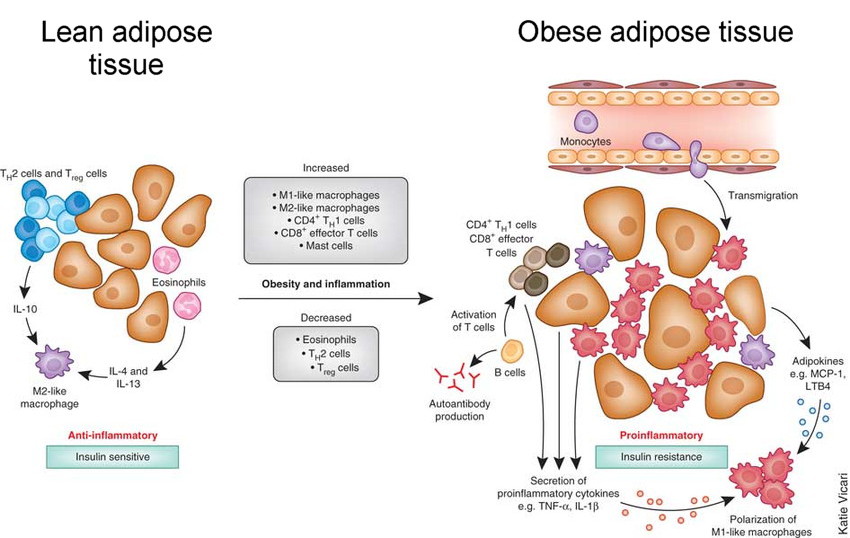
7. Obesidad
Nuestro sistema inmunológico evolucionó para protegernos de cosas que podrían dañarnos. Entonces, tal vez no debería sorprendernos que tener un exceso de grasa corporal desencadene la respuesta inflamatoria del sistema inmunológico.
En el tejido adiposo magro (grasa), las células del sistema inmunológico reparan el tejido y protegen contra los patógenos. Este es un entorno antiinflamatorio y sensible a la insulina.
Como puede ver en la imagen a continuación, los adipocitos individuales (células grasas) aumentan de tamaño a medida que uno tiene más sobrepeso. A medida que crecen los adipocitos y aumenta el estrés celular, el entorno se vuelve proinflamatorio y resistente a la insulina, lo que a menudo conduce a la condición de diabetes tipo 2.
8. Condiciones autoinmunes
There are more than 100 recognized autoimmune conditions—defined as conditions in which your immune system mistakenly attacks your body’s own cells. This causes inflammation in certain parts of the body or throughout the body. Some common autoimmune conditions are celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, lupus, fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, endometriosis, multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, chronic Lyme disease, narcolepsy, peripheral neuropathy, and thyroid diseases.
Los investigadores no saben exactamente qué causa las enfermedades autoinmunes y está claro que diferentes factores desencadenan enfermedades autoinmunes en diferentes personas. Los factores de riesgo incluyen:
- Una lesión o infección que no se resuelve
- Tener a alguien en su familia con una enfermedad autoinmune
- Tener sobrepeso
- De fumar
- Ciertos medicamentos
- Contaminación ambiental y toxinas químicas.
Another significant risk factor is being female. Overall, research shows that 75% to 80% of autoimmune condition sufferers are women. Researchers have identified a trigger for autoimmune conditions, called Age-associated B Cells, that may help explain why women tend to suffer from them more than men.
Taking steps to reduce sources of inflammation, like making changes in diet and reducing stress, are often effective in alleviating autoimmune conditions. If you suffer from an autoimmune condition, do your research, look at all 12 causes of inflammation in this post, and consider how you might be able to reduce inflammation in your body.
9. Variantes genéticas
While lifestyle is the most common cause of inflammatory conditions like heart disease and diabetes, certain inflammatory conditions like ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s Disease, ulcerative colitis, and psoriasis can be linked to genetic markers. And researchers have identified a gene called AUF1 that is linked to inflammation, accelerated aging, and cancer.
Though it can be exciting to think that discovering a causative genetic factor could bring us closer to curing certain diseases, it’s important to keep in mind the lessons that the burgeoning field of epigenetics is teaching us. While we may be genetically predisposed to certain diseases, whether or not those genes get turned on or off is heavily influenced by our lifestyle and environment.
10. Infecciones virales y bacterianas.
When a viral or bacterial infection doesn’t resolve on its own or with medical treatment, chronic inflammation can occur. Certain viruses tend to be difficult for our immune system to fight off (like HIV-1 and herpes), others can lay dormant and reoccur, and others can interfere with our immune response. The use of antibiotics, while often life-saving, has led to the development of antibiotic resistant bacteria—bacteria that are much more difficult to kill. Sometimes, an infection can even trigger an autoimmune condition.
Estos riesgos nos dan más razones para evitar infecciones contagiosas, obtener el tratamiento médico adecuado lo antes posible y descansar para permitir que nuestro sistema inmunológico haga su trabajo.
11. Alergenos y toxinas en los alimentos que comemos
Si es alérgico a un determinado alimento, probablemente ya lo sepa. Las intolerancias pueden ser más difíciles de identificar; es posible que deba realizar un seguimiento de sus síntomas y experimentar con dietas de eliminación para aislar al agresor. Vale la pena tomarse el tiempo para averiguar qué alimentos desencadenan la respuesta inmunitaria en su cuerpo, porque comer estos alimentos con regularidad puede dañar el revestimiento de su intestino, causar problemas digestivos inflamatorios y provocar síntomas inflamatorios en todo el cuerpo que quizás no crea. relacionados, como fatiga, erupciones cutáneas, dolores de cabeza y problemas neurológicos.
Además, hay muchas toxinas que se agregan a los alimentos, se utilizan en la producción y el envasado de alimentos, y se encuentran en los alimentos como resultado del medio ambiente que causan inflamación y aumentan el riesgo de desarrollar enfermedades inflamatorias como el cáncer. Éstos incluyen:
- Pesticidas
- Aditivos alimentarios, conservantes y colorantes.
- Aceites vegetales y de semillas refinados
- Grasas trans
- Mercurio (que se encuentra en niveles altos en ciertos pescados)
- Organismos genéticamente modificados (OGM)
- Hidrocarburos aromáticos policíclicos (creados cuando se quema la grasa)
- Aminas heterocíclicas (creadas cuando la carne o el pescado se cocinan a fuego alto)
- Acrilamida (creada al freír alimentos con almidón)
- Dioxinas (se acumulan en los alimentos grasos)
- Bisfenol-A (BPA; se encuentra en latas y recipientes de plástico)
12. Exposición prolongada a irritantes, como aire contaminado o productos químicos industriales.
While most causes of chronic inflammation are avoidable, it can be nearly impossible to prevent yourself from being exposed to air pollution. And sadly, research shows how air pollution contributes to neuroinflammatory conditions including stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease. In addition, air pollution causes inflammation throughout the body, increasing the risk of heart disease and other inflammatory conditions.
Industrial chemicals can also be an issue if you live near certain types of manufacturing plants or if your job exposes you to chemicals. Toxic chemicals can cause chronic inflammation and conditions like cancer that sometimes develop years later. Exposure to certain pesticides and chemicals is the likely cause of Gulf War syndrome, which often consists of neurological problems, memory problems, fatigue, tumors, skin conditions, digestive issues, headaches, and muscle and joint pain.
Siempre tenga en cuenta los productos químicos potencialmente tóxicos a los que puede estar expuesto y haga todo lo posible para evitar las áreas con una fuerte contaminación del aire. Si sospecha que ha estado expuesto a un contaminante o químico dañino, hable con su médico de inmediato.