The Game Changers: Why Top Athletes Are Making a Big Change
Produced by Arnold Schwarzenegger, James Cameron, and Jackie Chan, The Game Changers debuted at the Sundance Film Festival in 2018. I was lucky to see the movie when it came to theaters nationwide for a special one-day event on September 16th, 2019. If you missed it, not to worry—it’s coming to digital on October 1st.
James Wilks is an elite special forces trainer and winner of The Ultimate Fighter. After suffering a knee injury, he began doing in-depth research on how to speed his recovery. He came across a shocking study showing that the Roman gladiators ate mostly plant foods and very little animal protein.
This finding set James on a quest to find out if eating meat is necessary for protein, strength, and optimal health. His interviews with scientists, elite athletes, and soldiers, along with thousands of hours of research, showed him that everything he had been taught about animal protein was wrong.
If you’re interested in improving your athletic performance, increasing your energy, or simply improving your overall health—this movie is a must-see. If you want to learn more after reading this post, The Game Changers website provides easy-to-read scientific research explaining the health benefits of a plant-based diet—be sure to explore the sections on protein and all of the benefits.
What are humans meant to eat?
Now that the negative health effects of our highly-processed modern diet are widely accepted, everyone wants to know: What are humans meant to eat? What did we eat as we evolved?
Clearly, it wasn’t hot dogs, candy, and ice cream. We know for sure that our ancestors ate whole, unprocessed foods. But did we rely on plants (like vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds) or animals as our main source of sustenance?
To answer this question, all we need to do is look at our bodies. We have the digestive system of herbivores: Our long intestinal tract (about 9 times the length of our body) allows us to break down plants and absorb as many nutrients as possible.
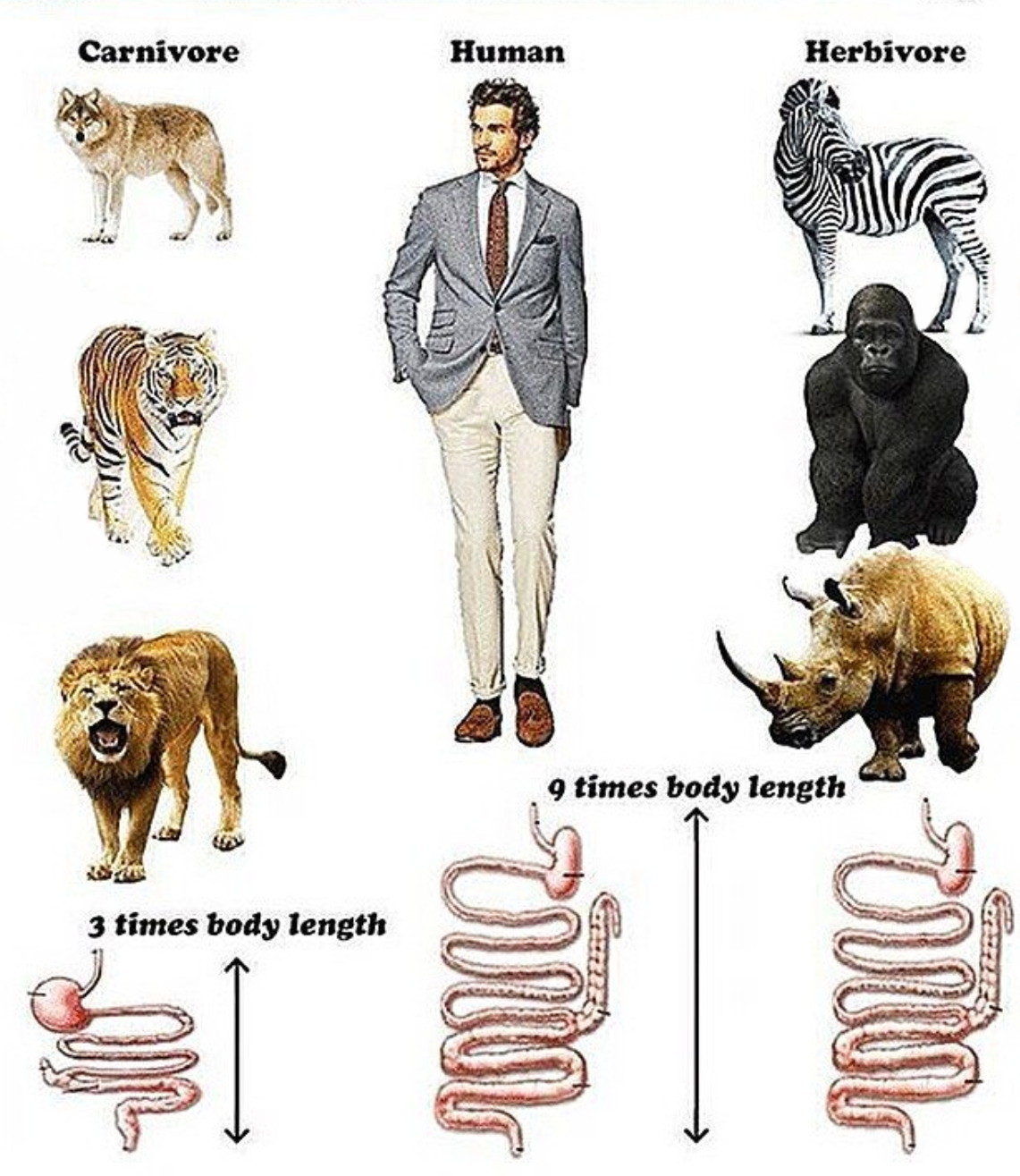
Carnivores, on the other hand, have a digestive tract about 3 times the length of their body. Their short digestive tract and their stomach’s strong hydrochloric acid extract nutrients from meat and get the waste out of their body within just a few hours.
When it comes to the mechanics of our digestive system, eating meat can pose health risks. It’s estimated that up to 12 grams of protein can escape digestion. As Dr. Michael Greger explains, when animal protein reaches the colon, it can be turned into toxic substances like ammonia. This helps to explain why eating meat increases our risk of developing colon cancer and other digestive system conditions—our digestive system simply isn’t designed to process large amounts of meat.
As you can see in the table below, humans are a specific type of herbivores—frugivorous herbivores—as are our closest animal relatives, chimpanzees and bonobos. Our flat teeth and entire digestive system are that of an animal whose primary physiological foods are fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, roots, and legumes.
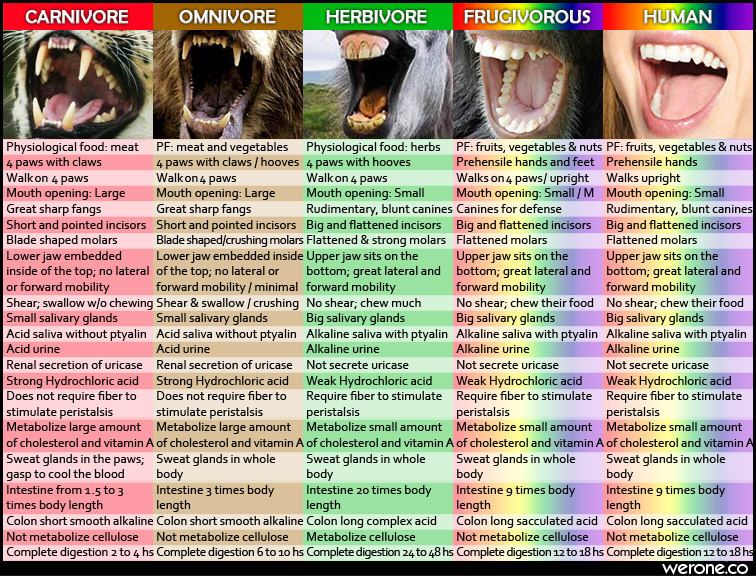
Humans began to eat meat as a survival mechanism when we migrated to areas of the world that didn’t offer enough plant foods to sustain us. But there’s no denying our biology—we simply aren’t designed to eat animal products on a regular basis.
Busting the protein myth
We’ve always been told that we need to eat meat and eggs so that we can get enough protein and the right kind of protein in our diets. Research shows that this is a myth.
Protein is made up of amino acids, and the human body requires 20 different amino acids in order to function properly. Our body makes 11 of these amino acids, so we don’t need to eat them. The other 9 are called the “essential” amino acids, because we need to get them from our food. While we’ve been taught that we need to eat meat in order to get these amino acids, it turns out that all plants contain the 9 essential amino acids in varying amounts.
We’re also under the impression that we need to eat vast amounts of protein in order to be healthy. But most of us don’t need to worry about protein consumption; the average American eats about twice as much protein as they need. And ironically, not only do vegetarians get about 70% more protein than they need, but meat-eaters get roughly half of their protein from plants!
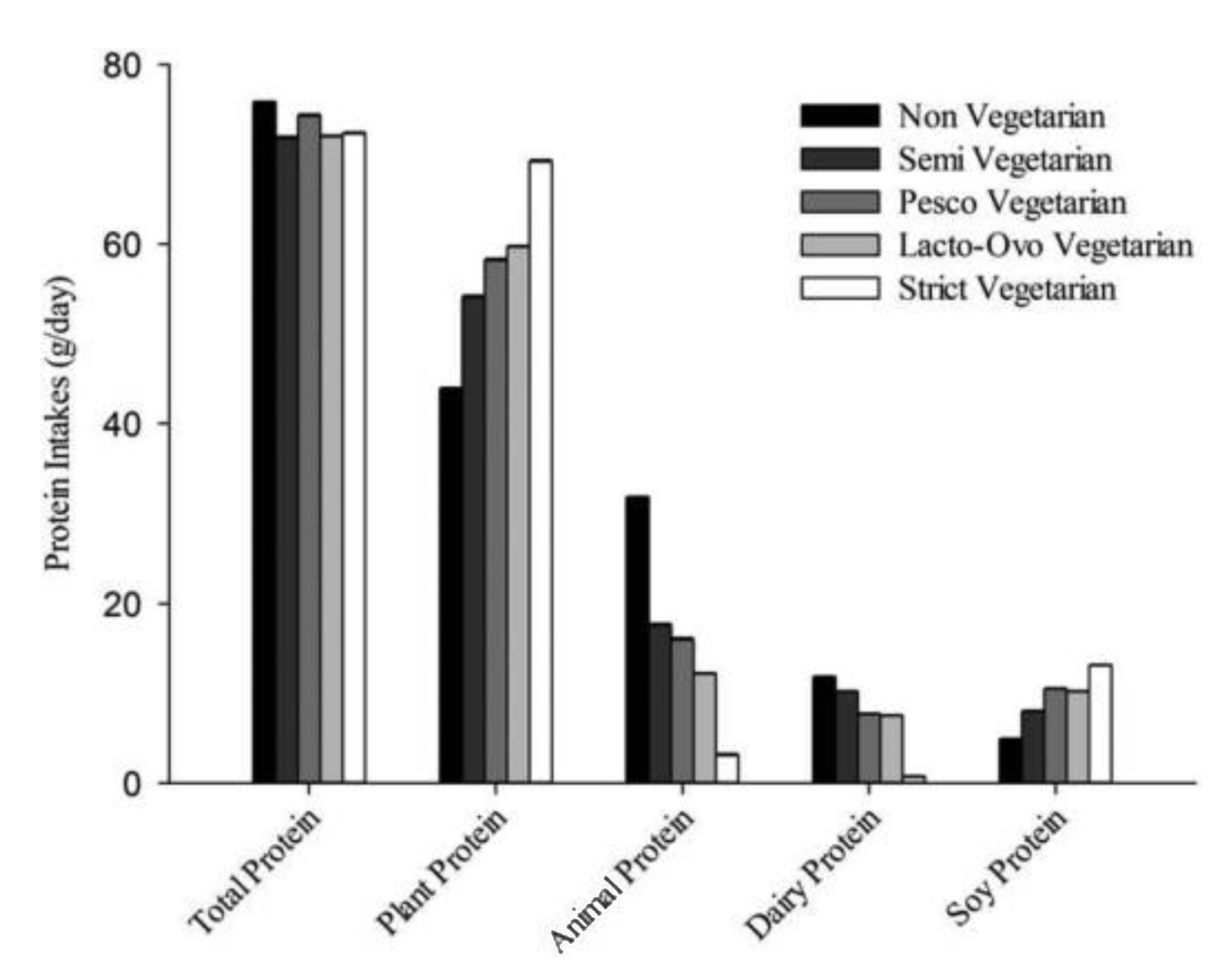
Rizzo NS, Jaceldo-Siegl K, Sabate J, Fraser GE. “Nutrient profiles of vegetarian and nonvegetarian dietary patterns.” Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. 2013 Dec;113(12):1610-9.
If you need any more proof, one of the strongest men in the world, Patrik Baboumian, is a vegan—and in The Game Changers you get to see him lift and flip a car.
Big benefits of a plant-based diet for athletes
As you’ll learn in the movie, there are four ways in which a plant-based diet improves athletic performance.
First, it provides optimal fuel for our muscles. When we eat carbohydrates, our body breaks them down into glucose (blood sugar), which is used as fuel for every cell in our body and brain. Unused glucose is stored as glycogen in our skeletal muscles and liver, and converted back to glucose when we need to use it for energy. Athletes need a great deal of glycogen to perform at high levels—this is why marathoners have big pasta dinners the night before a race. Even if you’re not an athlete, when you switch to a plant-based diet and start getting more of your calories from carbohydrates, you’ll likely feel more energetic both mentally and physically.
Second, it increases blood flow. Efficient blood flow is critical for athletes, as blood delivers oxygen and nutrients to our muscles. The Game Changers shows a blood test done on three NFL players after eating one meat-based meal compared to one plant-based meal, and the difference in blood thickness is shocking. Eating animal products also constricts blood vessels up to 40%, whereas plant foods contain healthy nitrates that signal our blood vessels to open.
Third, it makes muscles more efficient. The healthy nitrates found in plant foods not only signal our blood vessels to expand, but also allow our muscles to contract more efficiently. By using less energy per contraction, nitrates allow our muscles to perform longer using the same energy reserves.
Fourth, it speeds recovery by lowering inflammation. One of the top concerns of athletes is recovery time: The faster they can recover from a workout or injury, the sooner they can train again. Inflammation plays a big role in recovery. After a strenuous workout, our immune system kicks in to repair damaged cells. The more efficiently this process can take place, the sooner we feel ready for another strenuous workout.
Animal foods contain and lead to the formation of many toxic substances that increase inflammation and slow recovery time. Studies show significant increases in inflammatory markers just 1-2 hours after eating animal products. On the flip side, plants contain large amounts of anti-inflammatory substances like antioxidants. Not only does switching to a plant-based diet reduce measures of inflammation, but athletes report that it reduces soreness, speeds recovery from workouts and injuries, reduces tendinitis and joint pain, improves their immune system, and lengthens their athletic careers.
You can learn more about these topics in The Plant-Based Advantage.
Watch the trailer below to see great highlights from The Game Changers. And when you see the movie, you’ll get to see vegan ultra-runner Scott Jurek set the Appalachian Trail speed record, and three college athletes who find out that athletic performance isn’t the only kind of performance that improves on a plant-based diet. Be sure to check out The Game Changers when it comes to digital on October 1st!
Recommended reading:
The Pain Relief Secret: How to Retrain Your Nervous System, Heal Your Body, and Overcome Chronic Pain by Sarah Warren, CSE
Somatics: Reawakening the Mind’s Control of Movement, Flexibility and Health by Thomas Hanna
